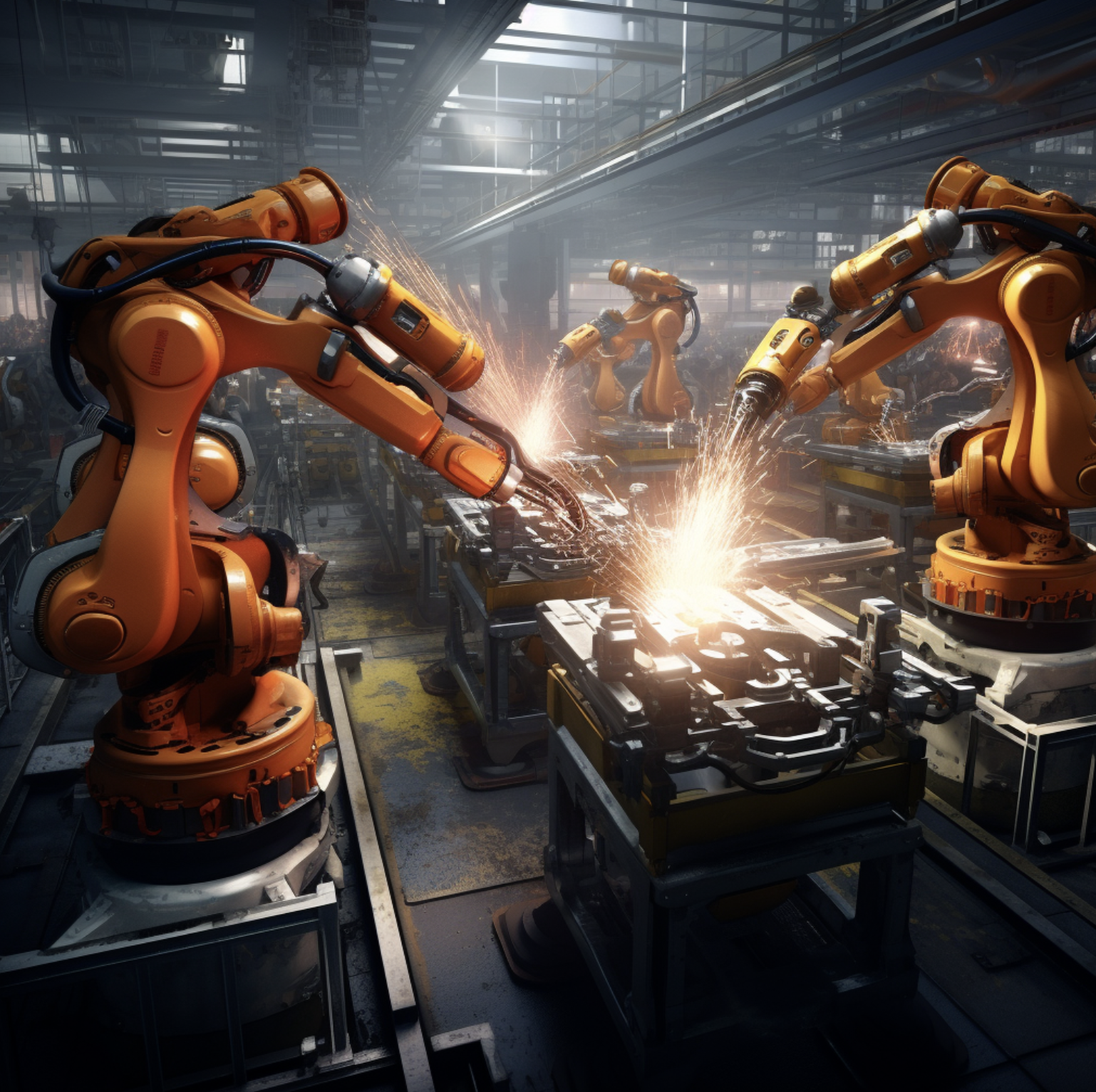
Robots have changed the way industries work. They bring efficiency and precision.
History of Robotics in Industry is rich and fascinating. Understanding this history helps us appreciate the technology we have today. From simple machines to complex systems, robots have evolved. Early industrial robots performed basic tasks. Over time, they became smarter and more versatile.
This journey highlights human ingenuity and the drive for progress. The introduction of robotics in industry began in the mid-20th century. Factories sought ways to improve production. Early robots, like Unimate, were game-changers. These machines could perform repetitive tasks with ease. As technology advanced, so did the capabilities of robots. Today, they are integral to manufacturing, assembly, and more. This history showcases the impact of robotics on industry growth.

Credit: robotics.kawasaki.com
Early Beginnings
The history of robotics in industry dates back to the early 20th century. These early stages laid the groundwork for the highly advanced systems we see today. Let’s explore the first concepts and early innovations that shaped the industry.
First Concepts
The concept of robots can be traced back to ancient myths and literature. Leonardo da Vinci sketched plans for a mechanical knight in the 15th century. This was one of the earliest recorded ideas of a human-like machine.
In the 1920s, Czech writer Karel Čapek introduced the term “robot” in his play “R.U.R.” (Rossum’s Universal Robots). This play imagined a future where artificial workers replace humans in industry. These early ideas inspired many inventors and engineers.
Early Innovations
The first practical industrial robot was the Unimate, developed by George Devol and Joseph Engelberger in the 1950s. This robot could handle hazardous tasks in factories, improving safety and efficiency.
By the 1960s, General Motors used Unimate robots in their production lines. These robots performed spot welding and other repetitive tasks. This marked the beginning of robotics in mass production.
Here’s a brief timeline of early innovations in industrial robotics:
| Year | Innovation |
|---|---|
| 1954 | George Devol patents the first industrial robot. |
| 1961 | General Motors installs the first Unimate robot. |
| 1969 | Victor Scheinman develops the Stanford Arm, a versatile robot arm. |
These early innovations paved the way for modern robotics. They demonstrated the potential of robots to transform industries. The journey from conceptual ideas to practical applications was challenging, but it set the stage for future advancements.
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Pioneering Technologies
In the early days of robotics, groundbreaking innovations laid the foundation for modern industry. These pioneering technologies changed how industries operate, making processes faster and more efficient. The journey began with the introduction of the first industrial robot. It paved the way for advancements we witness today.
Unimate And Beyond
The first industrial robot, Unimate, made history in 1961. Developed by George Devol and Joseph Engelberger, Unimate was a robotic arm. It performed repetitive tasks on the General Motors assembly line. Unimate’s success proved robotics’ potential in industry. This led to the creation of more sophisticated robots. These new robots could perform complex tasks with precision.
As technology advanced, robots became more versatile. They moved beyond simple tasks. Modern robots now handle welding, painting, and assembly. Industries like automotive, electronics, and manufacturing benefit greatly from these advancements. Unimate was just the beginning. Robotics continues to evolve and adapt to industry needs.
Influential Figures
Several key figures have shaped the history of industrial robotics. George Devol, an inventor, created the first programmable robot. Joseph Engelberger is often called the “father of robotics.” Together, they pioneered the introduction of robots into manufacturing.
Another notable figure is Isaac Asimov. He introduced the world to the term “robotics” through his science fiction works. His Three Laws of Robotics influenced how people think about robots. He inspired many engineers and scientists.
Hiroshi Ishiguro, a modern-day roboticist, is known for his work on humanoid robots. His research pushes the boundaries of what robots can do. These influential figures have all contributed to the advancement of robotics in industry. Their work continues to inspire new generations of innovators.
Rise Of Automation
The rise of automation has transformed industries worldwide. It brought significant changes to manufacturing. Automation introduced efficiency and precision. This resulted in higher productivity and lower costs. The history of robotics in industry highlights key advancements that shaped modern production.
Advent Of Cnc Machines
Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines emerged in the 1950s. They automated machining processes, increasing accuracy and speed. CNC machines used computers to control machine tools. This allowed for intricate designs and consistency in production. The advent of CNC machines marked a major step in industrial automation.
Integration In Production Lines
Robotics soon integrated into production lines. This integration started in the automotive industry. Robots performed repetitive tasks with precision. They reduced human error and improved safety. Over time, more industries adopted robotic integration. This led to faster and more efficient production processes.

Credit: www.tdk.com
Robotics In The 21st Century
Robotics in the 21st century marks a new era in industrial automation. The integration of robotics has transformed industries, enhancing productivity and efficiency. This century has seen rapid advancements in technology, making robots smarter and more adaptable. From simple tasks to complex operations, robots have become indispensable in various sectors.
Advancements In Ai
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has significantly impacted robotics. Modern robots can now perform tasks with precision. AI enables robots to learn and adapt to new environments. This makes them more efficient and reliable. Machine learning and deep learning algorithms power these intelligent systems. They analyze data, recognize patterns, and make decisions. This improves the overall performance of industrial robots.
Collaborative Robots
Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside humans in various industries. They are designed to be safe and user-friendly. Cobots help in tasks that require human-robot interaction. They enhance productivity and reduce human effort. These robots are equipped with sensors to ensure safety. Cobots can be easily programmed and reprogrammed. This flexibility makes them ideal for small and medium-sized enterprises.
Impact On Workforce
The history of robotics in industry has brought significant changes to the workforce. Robots have transformed jobs, altered skill requirements, and influenced work environments. Understanding these impacts helps us prepare for the future of work in an automated world.
Job Transformation
Robots have changed many jobs in industries. Some roles have been replaced, while new ones have emerged. This transformation has led to a shift in job responsibilities.
- Assembly line workers now manage and monitor robots.
- Technicians repair and maintain robotic systems.
- Quality control roles focus on ensuring robots perform tasks correctly.
Many repetitive tasks are now automated. This allows workers to focus on more complex and creative tasks. The nature of work has evolved, leading to more efficient and safer workplaces.
Skill Requirements
The rise of robotics in industry has changed the skills needed for many jobs. Workers must adapt to new technologies to stay relevant. This shift has created a demand for new skill sets.
- Technical skills: Understanding and operating robotic systems.
- Programming skills: Writing and updating software for robots.
- Analytical skills: Analyzing data from robots to improve processes.
Training and education are crucial in this new landscape. Workers need continuous learning to keep up with advancements. Companies invest in training programs to help employees adapt. This investment ensures a skilled workforce ready for the future.
Economic Implications
The history of robotics in industry is rich with innovation and change. Beyond the technological advancements, the economic implications are profound. Robotics have reshaped industries, creating new opportunities and challenges. Understanding these economic impacts can help businesses adapt and thrive.
Cost Efficiency
Robots have significantly reduced operational costs. They perform tasks faster and with precision. This reduces waste and errors. Maintenance costs are also lower due to fewer breakdowns. Over time, this leads to substantial savings for companies. It allows them to allocate resources more effectively.
Market Growth
The use of robotics has spurred market growth. New markets have emerged around robotics technology. Companies develop and sell robots for various industries. This creates jobs and stimulates economic activity. The increased productivity from robots also drives demand for goods and services. As a result, economies expand and evolve.
Future Trends
The history of robotics in industry is fascinating. As technology evolves, the future trends in industrial robotics will shape many sectors. These trends include innovations like smart factories and sustainability initiatives. Let’s explore these trends.
Smart Factories
Smart factories are the future of industrial robotics. They use advanced technologies to improve production. These factories integrate robotics, IoT, and AI.
Key features of smart factories:
- Automated workflows
- Real-time data analysis
- Predictive maintenance
Automated workflows reduce human error. They ensure tasks are completed efficiently. Real-time data analysis helps in making quick decisions. Predictive maintenance reduces downtime. It predicts equipment failures before they happen.
Smart factories are flexible. They can quickly adapt to changes. This is essential in today’s fast-paced market. Smart factories are not just a trend. They are the future of manufacturing.
Sustainability Initiatives
Sustainability is a growing focus in industry. Robotics can help achieve these goals. Sustainable practices in factories reduce waste and save energy.
Benefits of sustainability initiatives:
- Reduced carbon footprint
- Energy-efficient processes
- Waste minimization
Robots can perform tasks with high precision. This reduces material waste. They also operate efficiently, consuming less energy. Robots can work in hazardous environments. This reduces the need for human intervention.
Implementing sustainability initiatives is crucial. It helps in meeting environmental regulations. Sustainable factories are not just better for the planet. They are also cost-effective in the long run.
Challenges And Solutions
The history of robotics in industry reveals both challenges and solutions that have shaped its evolution. As robots became integral to industrial processes, addressing these challenges became crucial. This section explores two significant challenges: cybersecurity risks and ethical considerations. Understanding these aspects is essential for the continued advancement of robotics in industry.
Cybersecurity Risks
Cybersecurity risks pose a major challenge in the realm of industrial robotics. Robots connected to networks are vulnerable to cyber-attacks. Hackers can exploit these vulnerabilities to disrupt operations. Such disruptions can lead to financial losses and safety hazards. Protecting these systems from cyber threats is critical.
Companies invest in robust cybersecurity measures. Regular software updates are essential. Firewall protections and encryption also play a vital role. Training employees on cybersecurity best practices is equally important. These steps help mitigate the risks associated with cyber threats.
Ethical Considerations
Ethical considerations are another significant challenge in the use of robots in industry. The deployment of robots impacts employment. Some fear job losses due to automation. Balancing technological advancement with job preservation is a delicate task. Ensuring fair labor practices is essential.
Transparent communication between companies and employees is key. Engaging in open discussions about the impact of automation helps. Offering retraining programs for displaced workers provides solutions. Ethical considerations must be addressed to ensure sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The History Of Robotics In Industry?
The history of robotics in industry began in the 1950s. The first industrial robot, Unimate, was introduced in 1961. Since then, robots have evolved, becoming integral to manufacturing and production processes.
How Did Industrial Robotics Start?
Industrial robotics started with the invention of Unimate in 1961. It was the first robot used in a General Motors factory. This marked the beginning of robots being used for repetitive and hazardous tasks.
Why Are Robots Important In Industry?
Robots are important in industry for their efficiency and precision. They perform repetitive tasks accurately and handle dangerous jobs safely. This increases productivity and reduces human error.
What Are The Key Milestones In Industrial Robotics?
Key milestones include the introduction of Unimate in 1961, the development of SCARA robots in the 1980s, and the integration of AI in recent years. These advancements have significantly improved robotics capabilities.
Conclusion
Robotics in industry has a rich and fascinating history. From early automation to advanced AI, robots have transformed manufacturing. They boost productivity, enhance precision, and ensure safety. As technology advances, robots will continue to shape industries worldwide. Understanding this history helps us appreciate modern innovations.
Stay curious and keep learning about robotics. The future holds even more exciting developments.